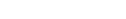A strong economy system can influence player behavior, enhance player progression, and ultimately contribute to the success of a video game. In-game economies can be complex and require careful planning to ensure a well-balanced system. In this guide, we will discuss key elements in designing and managing a game’s economy, with hypothetical examples to illustrate best practices.
1. Build Economic Systems
To build a strong in-game economy, it is important to understand real-world economies and how they function. This can be done by researching economic principles and studying successful game economies in the gaming industry. Take note of the most complex-looking game economies, such as those found in strategy simulation games like Civilization VI or Age of Empires II. These games simulate real-world economies and can serve as a valuable reference for designing your own.
The way a game’s economy is built can also greatly impact its gameplay. For example, games with an open-ended sandbox setting often have player-driven economies, where players can trade and set their own prices for goods and services. On the other hand, games with a more linear storyline may have an economy that is driven by scripted events and quests.
Before you begin designing your game’s economy, consider the type of gameplay and setting you want to create. This will help determine what kind of economic system would work best for your game. A holistic approach to designing your game’s economy will ultimately lead to a more cohesive and engaging gameplay experience for players.
Creating a mind-map and running simulations can also be helpful in visualizing and testing different economic systems before implementing them in the actual game. This will help you identify any flaws or imbalances in the system and make necessary adjustments.
2. Make Sure Your In-Game Currency Has Value
The best games give their virtual currencies value by making them in-demand by NPCs (non-playable characters) and players alike. This creates a sense of scarcity and drives players to actively participate in the game’s economy. Skyrim’s gold currency, for example, is highly valuable because it is used to purchase useful items such as weapons and armor from NPCs.
Additionally, hiring allies is also possible with the use of in-game currency. This adds another layer of value to the currency, as players can use it not only for personal gain but also for strategic purposes within the game. Consider not only the in-game products but the services and opportunities that can be purchased with your virtual currency. This will make the currency feel more tangible and valuable to players.
Be creative with the use cases of your virtual currencies. You can take real world use cases as inspiration. For example, it may be cheaper to walk or you can hire an Uber for transportation in the real world. Is there a fast travel system in your game? If so, players can pay for convenience and save time by using their virtual currency to fast travel.
3. Economic Stability Matters In Your Game
What is the total supply of your virtual currency? How often is it distributed in the game? These are important factors to consider when designing the economic stability of your game. If there is an infinite supply of virtual currency, it can lead to inflation and devalue the currency over time.
On the other hand, if the currency is too scarce and difficult to obtain, it can create frustration for players and discourage them from participating in the economy. It is important to strike a balance and carefully manage the distribution and availability of your virtual currency.
Consider implementing systems such as taxes or fees for in-game transactions to regulate the flow of currency. This can also add a layer of realism to your game and create a more dynamic economy. Much like any economy, it can be difficult to program an exact balance, but monitoring and adjusting the system over time can help maintain a stable economy.
4. Create Immersive Experiences with Your Economy
There are different ways to incorporate your virtual economy into the overall gameplay experience. One popular method is through in-game stores where players can purchase items or upgrades using their virtual currency.
But think beyond just buying and selling goods. You can also create immersive experiences by tying in-game challenges or quests to earning or spending virtual currency. For example, players may need to pay a fee to enter a certain area of the game or complete a task within a time limit for a large sum of virtual currency.
You can also use virtual currencies as a means of social status within the game. Implementing leaderboards or exclusive items that can only be purchased with large amounts of virtual currency can create a competitive atmosphere and motivate players to earn more. Some items may just be aesthetically pleasing, while others may provide gameplay advantages, creating a demand for certain items and driving the economy.
Another way to make your virtual economy more immersive is by introducing elements of scarcity and rarity. This can be done through limited edition items or events that offer rare rewards in exchange for large amounts of virtual currency. This can create a sense of urgency and exclusivity among players, driving them to participate in these events and increasing the value of their virtual currency.
5. Have Your Most Valuable Items Priced Appropriately
A common mistake that game designers make is not properly pricing their most valuable items. These items are often the ones that players desire the most, whether for gameplay advantages or simply for bragging rights.
To ensure a healthy virtual economy, it’s important to carefully consider the prices of these high-value items. They should be expensive enough to maintain their exclusivity and desirability, but not too expensive that they become unattainable for the majority of players. It’s a delicate balance, but adjusting prices based on player feedback and market trends can help maintain a healthy economy.
In addition to pricing, it’s also important to consider how these high-value items are obtained. They should not be easily attainable, as this could lead to an oversaturation of the market and decrease their value. Instead, they should require a significant amount of effort or skill to obtain, making them truly valuable in the eyes of players.
Imagine if only one store carried an item. That item should be more expensive compared to a general store with multiple locations. This same concept applies to virtual items in a game – if an item is rare and difficult to obtain, it should be priced accordingly. The scarcity and exclusivity of these items will only increase their perceived value among players.
6. Deploy Strategic Planning For The Future
Game developers should consider how their virtual economy will evolve over time. As players progress and new content is added, the value of certain items may fluctuate. Therefore, it’s important to have a long-term plan in place for managing the economy.
One strategy is to regularly introduce new, high-value items into the game to keep the market fresh and maintain player interest. This can also help balance out any inflation that may occur as players accumulate more virtual currency.
Another key aspect of strategic planning is anticipating potential exploits or loopholes in the economy system. It’s important to continuously monitor and adjust prices and item availability to prevent players from exploiting these weaknesses for personal gain. If there is a quest that is too easy and rewards players with a large sum of virtual currency, for example, it may need to be adjusted to maintain balance in the economy.
7. Consider Monetization Opportunities
Real-world money is often exchanged for virtual currency or items in games, creating a form of virtual economy within the larger gaming industry. Developers should consider incorporating monetization opportunities into their game design to further enhance the virtual economy.
This can include offering exclusive cosmetic items for purchase, implementing a subscription model that provides players with a steady stream of virtual currency, or even allowing players to trade real money for in-game goods and services. However, it’s important for developers to strike a balance between making these options available without turning the game into “pay-to-win.”
By carefully considering these strategies and continually monitoring and adjusting the virtual economy, game developers can create a thriving and balanced in-game economy that enhances the overall gaming experience for players. With a well-designed virtual economy, players will not only have more fun playing the game, but they may also be more likely to continue playing and investing their time and money into it.
8. Don’t Neglect Resource Management
Your most valuable resources in the game may be virtual currency and rare items, but don’t overlook the importance of properly managing other resources as well. This includes things like time, energy, and storage space.
Players should feel like they have a good balance of earning and spending in the game. If it takes too long to earn virtual currency or the cost of items is too high, players may become frustrated and lose interest. On the other hand, if it’s too easy to acquire resources, players may quickly reach a point where they have nothing left to work towards.
Resource management also ties into game design and balancing. Developers should carefully consider how much time and effort it takes for players to obtain certain resources and how those resources can be used in the game.
9. Consider Secondary Markets
With the rise of cryptocurrencies and Web3 technology, secondary markets for virtual items have become more prevalent. Some players may be willing to pay real money for rare or exclusive items in a game. Will people only play just for the sake of obtaining an item so they can sell it? And if so, would this make the game feel more like work rather than play? These are all important considerations when designing a virtual economy.
Game developers should consider the impact of these secondary markets on their virtual economy and whether they want to allow or regulate them. On one hand, it can provide an additional source of revenue for developers. On the other hand, it may introduce potential legal issues and create imbalance among players who can afford to purchase items versus those who cannot.
If an item provides OP (over-powered) advantages or disrupts game balance, it may be necessary to regulate its availability in secondary markets. This can also help prevent those with more capital to obtain and essentially ‘Rule’ the game, leading to a negative player experience.
10. Use Analytics For Better Game Economy Management
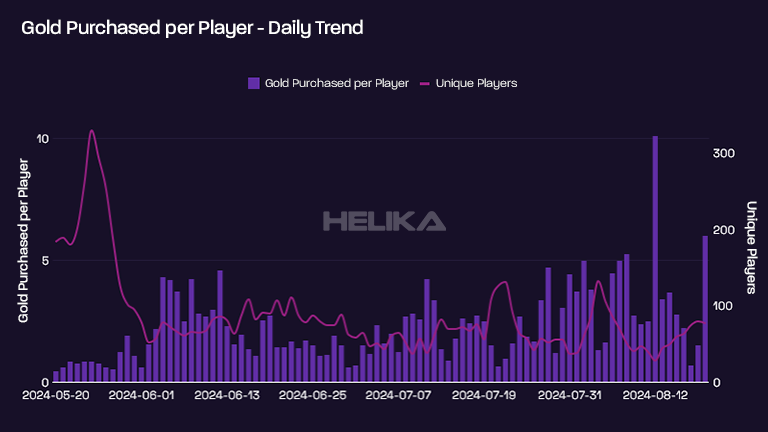
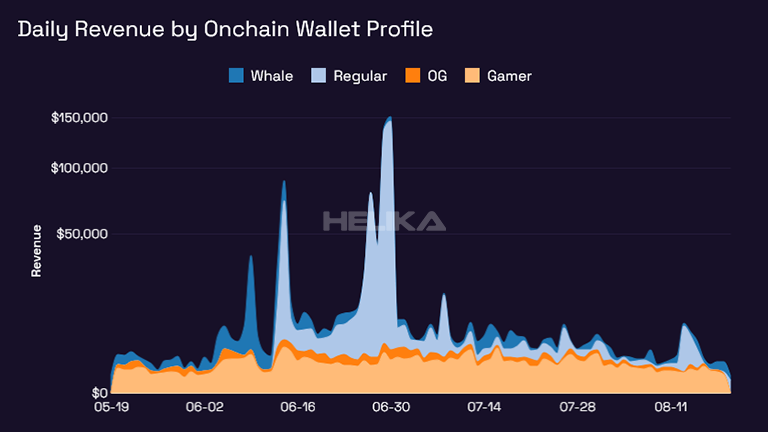
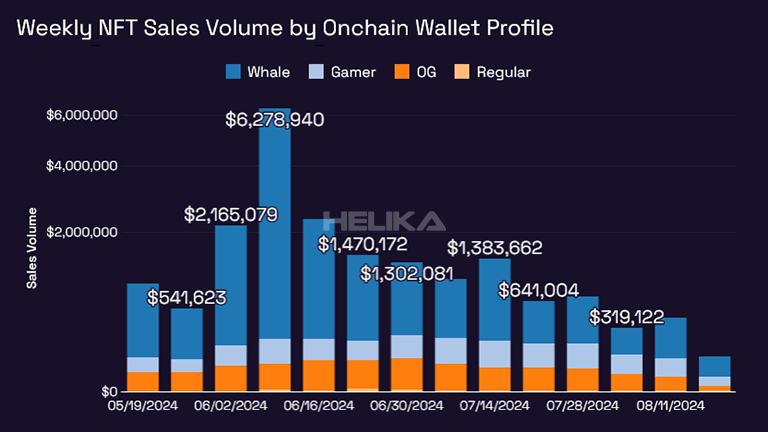
To get a competitive advantage, using analytics provided by a team with professional training can make a significant impact on the effectiveness of your in-game economy. Helika plays a crucial role for game developers as we find the latest trends in your game’s virtual economy through data analysis. We can help you understand the behavior of your players and how they interact with your in-game economy, allowing you to make informed decisions on what changes or adjustments need to be made.
Analytics can also help identify potential issues in the game economy, such as inflation or deflation of in-game currency. This information can then be used to make necessary tweaks and adjustments to maintain player retention and increase revenue for game studios. There are a lot of things that can hinder a game’s economy, and analytics can help pinpoint the root cause of these issues.
Furthermore, using analytics can also provide insights into player spending habits and preferences. This is a good thing as you’ll receive insights on the right time to introduce new items or features in your game’s economy. It can also help identify which items are popular among players and adjust pricing accordingly (remember point 5? consider this a more advanced version).
Final Thoughts
Building an immersive in-game economy is no easy task. The best way to do so is to keep in mind these best practices, run simulations, and adjust accordingly. With the leading game analytics partner in Helika, you can create and maintain a successful in-game economy that keeps players engaged and satisfied.
Utilizing analytics not only helps with revenue and player retention but also allows for constant improvements to keep your game relevant and exciting. So why wait? Start using Helika’s analytics services today and take your in-game economy to the next level. Feel free to contact us for any queries or assistance.